Recent Posts
Thyroid disease: Learn the types, symptoms and treatments

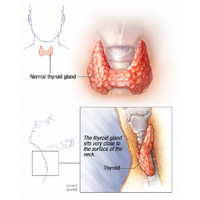
Most people have heard of the thyroid gland, but many do not know or understand what it does. The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland. It makes hormones called thyroid hormones, which help regulate the body's metabolism. The gland is shaped like a butterfly and is located in the front of the neck below the Adam's apple.
Problems occasionally can occur in the thyroid gland, with the most common being overactivity and underactivity.
What is hypothyroidism?
One of the most common problems affecting the thyroid gland is hypothyroidism. This condition occurs when the gland stops making enough hormone. The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder that ultimately causes the gland to stop working. In early stages, hypothyroidism may not cause noticeable symptoms.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism may vary, and can include:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Coarse hair and skin
- Muscle weakness
- Slowed heart rate
Hypothyroidism is treated with thyroid hormone medicine that is effective when taken at the correct dose. If left untreated, hypothyroidism can lead to high cholesterol and heart problems over time.
What is hyperthyroidism?
Some disorders of the thyroid gland cause it to be overactive and make too many thyroid hormones, a condition called hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism usually is caused by an autoimmune disease called Graves' disease. It also can be caused by a metabolically active thyroid nodule making too much hormone or by a short-lived thyroid gland inflammation. Graves' disease can be treated with medication, radioactive iodine therapy or surgery. Graves' disease can lead to Graves' ophthalmopathy, or thyroid eye disease, which can cause vision loss, eye pain or bulging eyes.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism also vary and can include:
- Losing weight without trying
- Rapid heart rate
- Sweating
- Diarrhea
- Nervousness
- Muscle weakness
- Thinning skin and brittle hair
Other thyroid disorders
Other disorders of the thyroid gland often require surgery for treatment. A thyroid lobectomy, known as hemilobectomy, is a surgery that removes part of the gland. During a total thyroidectomy, the entire gland is removed. Thyroid cancer treatment usually requires total thyroidectomy and, in some cases, removal of lymph nodes in the neck. Many small thyroid cancers can now be treated with a lobectomy.
Some noncancerous nodules become large enough to cause pain and problems swallowing and breathing. When this happens, partial or total thyroidectomy is recommended. A person who has part of their thyroid gland removed may need to take hormone replacement after surgery. When a person has the entire gland removed, they will need to take replacement hormones for life.
When to seek treatment for thyroid symptoms
Consider seeing your primary care professional if you have signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, or if you can feel a nodule in the lower front of your neck. Your healthcare team will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical exam. Your care may include lab tests, a neck ultrasound and referral to an endocrinologist or an ear, nose and throat specialist. If surgery is needed, you will be referred to an ear, nose and throat surgeon or general surgeon with expertise in performing thyroid procedures who will evaluate and discuss your options.
Thyroid disorders are relatively common in adults. Fortunately, nearly all thyroid problems can be managed successfully when identified early.
Omar El Kawkgi, M.B., B.Ch., is an endocrinologist in Eau Claire, Wisconsin.